Rather than adapting the prosthesis to available components, align the abutment design with restorative intent.
Restorative-Driven Implant Abutment Planning
SMART 1 implant abutments are proprietary dental lab-designed restorative components developed by Burbank Dental Lab to support implant-supported restorations through restorative-driven planning.
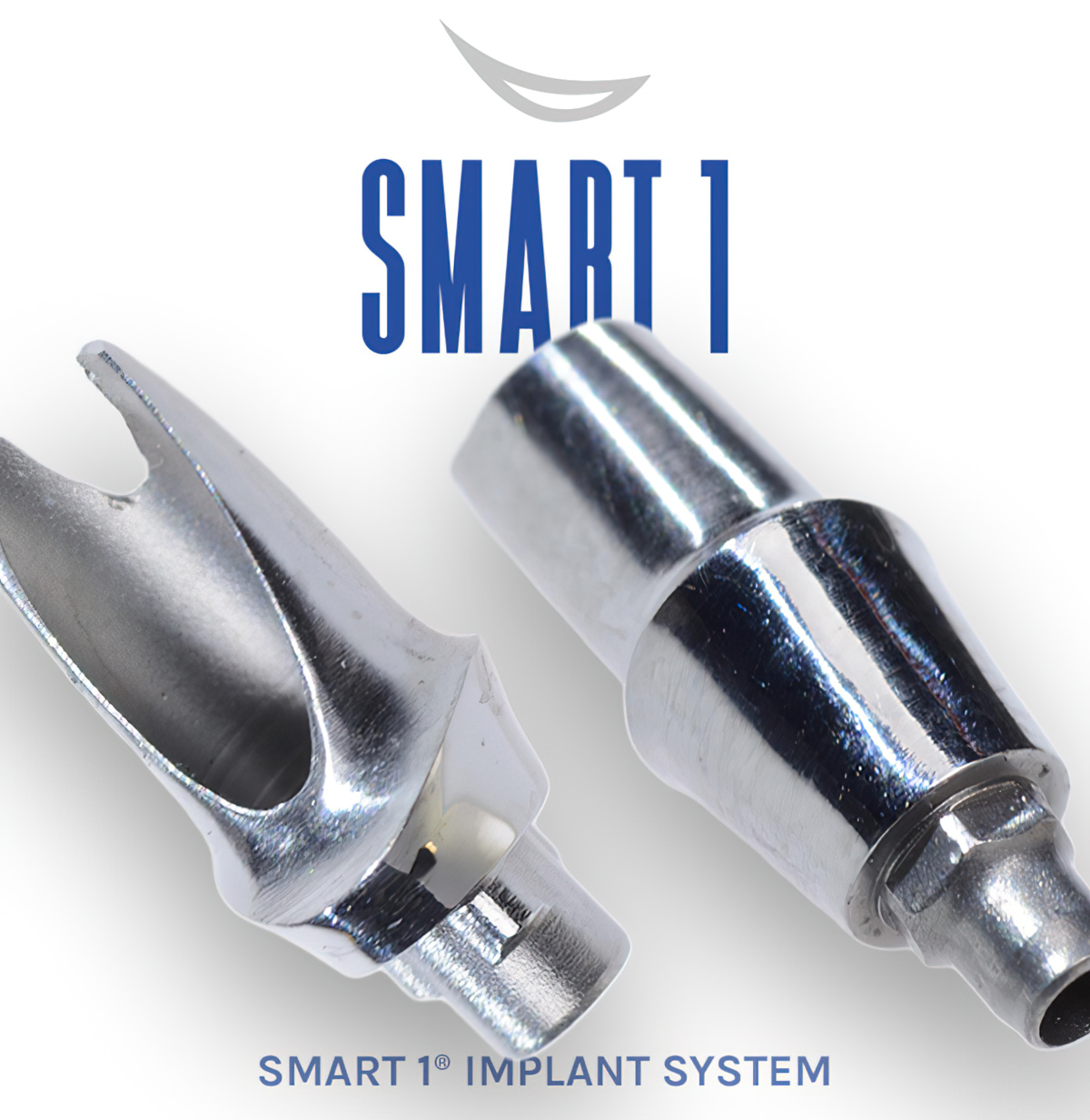

They are not intended as universal replacements for stock or multi-unit abutments, but rather as case-specific components used when prosthetic requirements benefit from coordinated design between the clinician and the lab.
Within the implant restorative sequence, SMART 1 abutments are introduced after implant placement and osseointegration and before fabrication of the definitive prosthesis. Their primary function is to establish a controlled restorative interface between the implant fixture and the final restoration—one that reflects the intended prosthetic contours, emergence profile, and restorative space requirements established during treatment planning.
Rather than adapting the prosthesis to available components, the SMART 1 approach prioritizes aligning abutment design with restorative intent. This distinction is particularly relevant in digitally planned cases, where prosthetic parameters can be defined early and translated directly into component design.
Indications and Case Selection
SMART 1 abutments are indicated when restorative demands exceed the capabilities or limitations of standardized components. Case selection is driven by prosthetic requirements, not by implant brand preference or component availability.
Restorative space considerations
Limited vertical or horizontal restorative space may necessitate abutment designs that are coordinated with the final prosthesis to avoid material compromise or overcontouring. Early identification of restorative space constraints allows abutment geometry to be planned accordingly.
Implant alignment and angulation
When implant placement results in angulation that complicates prosthetic path of insertion, occlusal alignment, or restorative design, a custom abutment strategy may be considered to re-establish a prosthetically favorable orientation.
Prosthetic complexity
Cases involving splinted restorations, full-arch prostheses, or specific restorative contours often benefit from abutment designs that are planned in parallel with the prosthesis rather than selected after the fact.
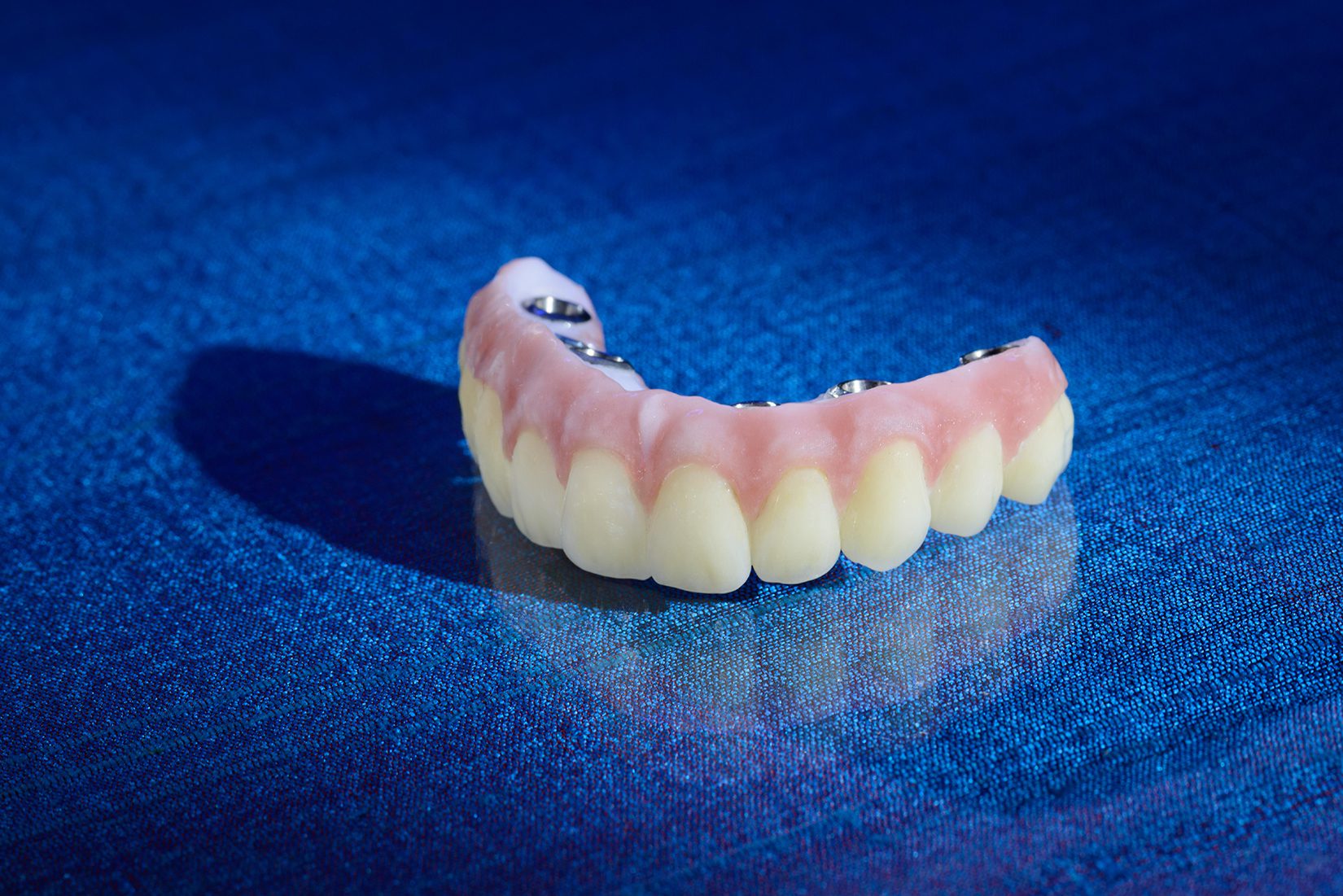
SMART 1 abutments are selected when diagnostic records, restorative goals, and prosthetic design considerations indicate that a coordinated, lab-driven approach may reduce downstream compromises.
Implant Digital Workflow Integration
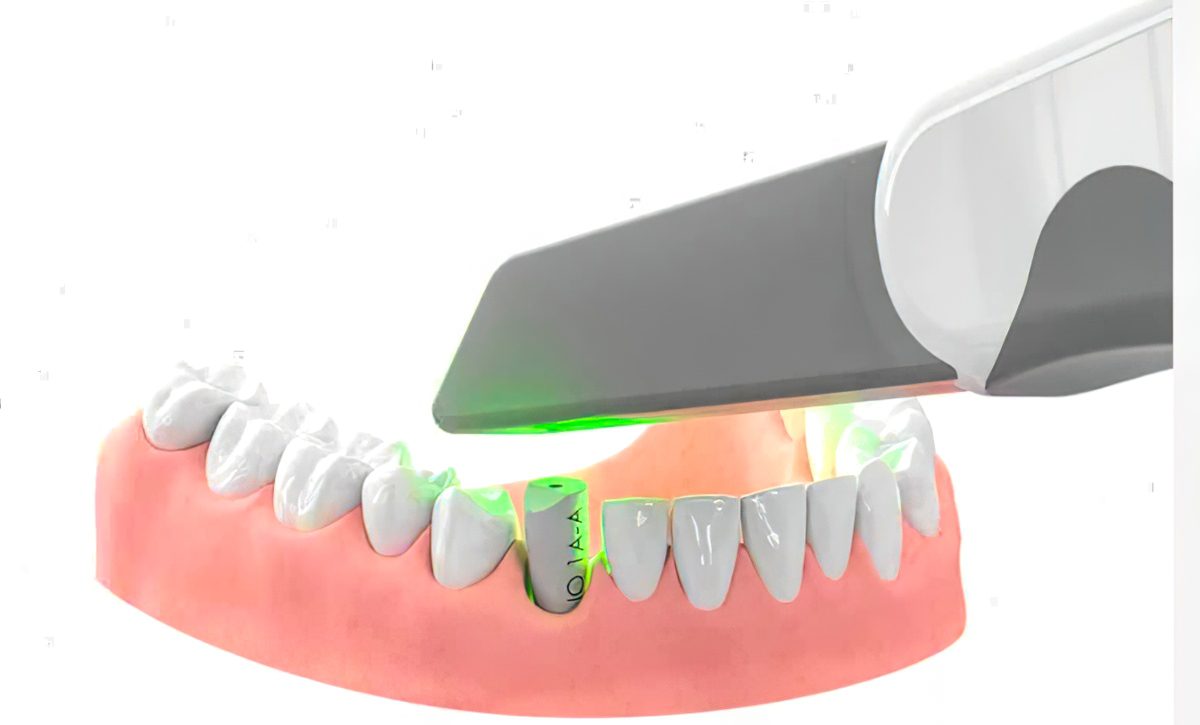
Revolutionizing Prosthetic Dentistry: The Benefits of Digital Denture WorkflowsSMART 1 abutments are planned within a digital workflow that emphasizes early collaboration between the clinician and the dental lab. Diagnostic data—including intraoral scans, CBCT imaging, and restorative design parameters—are used to inform abutment design before definitive prosthetic fabrication begins.
This workflow supports:
By integrating abutment planning into the digital workflow, restorative decisions are addressed proactively rather than reactively. The focus remains on process coordination and clinical communication, not on specific software or equipment.
The best abutment decisions happen before you need to make them.
Restorative and Prosthetic Considerations
Abutment design directly influences the geometry, fit, and maintainability of the final prosthesis. SMART 1 abutments are designed to support accepted prosthodontic principles rather than assumed clinical outcomes.
Emergence profile planning and development
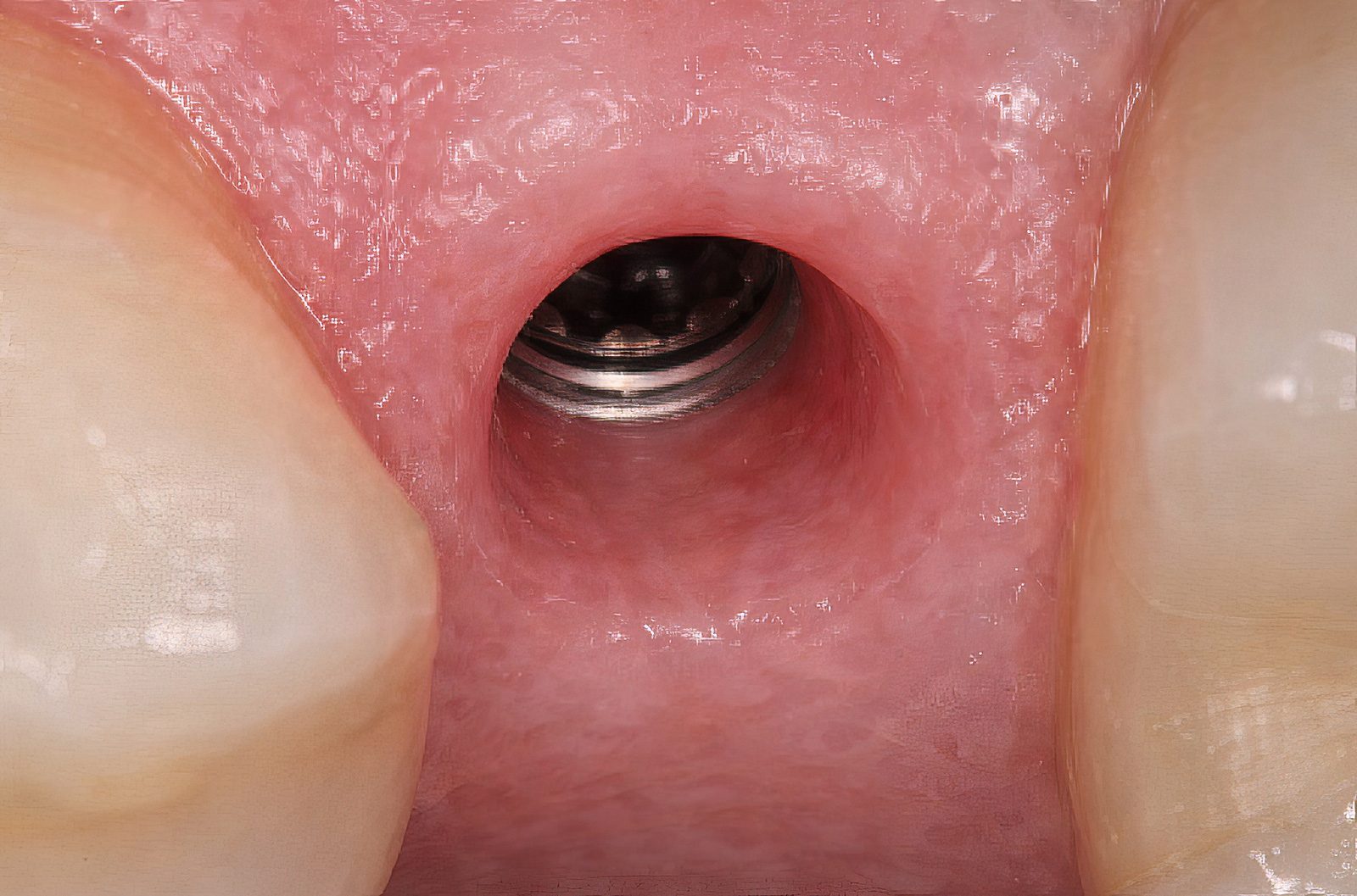
Abutment contours influence how the prosthesis transitions from the implant platform to the restorative margin. Controlled emergence profile planning supports prosthetic contours that respect peri-implant tissue architecture and restorative design intent.
Hygiene access and cleansability
Abutment geometry is planned with consideration for patient access and professional maintenance, particularly in splinted or full-arch restorations where hygiene challenges are common.
Prosthetic interface and fit
A coordinated abutment–prosthesis interface supports passive fit principles and reduces the need for compensatory adjustments during delivery.
Long-term maintenance considerations are addressed through design planning rather than predictive claims, recognizing that outcomes depend on multiple clinical and patient-specific factors.
Designing for More Predictable Case Outcomes
While no restorative system can guarantee clinical outcomes, case predictability can be improved through structured planning and collaboration. The SMART 1 workflow supports this by encouraging clinicians to address restorative variables early in the treatment process.
Predictability isn’t luck—it’s planning addressed proactively rather than reactively.
Key planning considerations include:
Define restorative intent before component selection
Establishing prosthetic contours, material selection, and occlusal scheme early allows abutment design to support the final restoration rather than constrain it.
Communicate prosthetic priorities early
Sharing restorative goals with the dnetal lab—such as emergence profile preferences, margin positioning, and hygiene considerations—allows these factors to be incorporated into abutment design.
Use digital reviews to identify conflicts early
Digital design review provides an opportunity to identify alignment, space, or access issues before fabrication, reducing the likelihood of late-stage adjustments.
These principles are not unique to SMART 1 abutments but are essential to restorative-driven implant dentistry. The SMART 1 system is designed to facilitate their consistent use through lab–clinician collaboration.
3 STEPS TO PHOTOGRAMMETRY SCANS
WE HELP YOU GET IT RIGHT EVERY TIME

STEP 1
Burbank Dental Lab implant scan specialist provides the special scan bodies for insertion in the patient’s newly placed implant sites.
STEP 2
Scan Bodies are removed and special healing abutments are placed on the implant sites. Soft tissue can now be scanned with an intra-oral scanner.
STEP 3
The data from both scans are then sent to the dental laboratory. The ICam4d data and soft tissue scans are aligned to become a high-precision dental model.
The Role of the Dental Lab
Burbank Dental Lab plays a crucial role in SMART 1 cases by acting as a technical partner. The lab supports restorative planning through design translation and workflow coordination.
This includes:
The strongest implant cases are built on lab-clinician communication, not just materials.
Lab-clinician implant coordination
The collaboration model focuses on shared responsibility and communication instead of prescriptive decision-making. The dental lab’s involvement aims to align surgical placement, abutment selection, and prosthetic fabrication.
FREE TO DOWNLOAD – SUCCESS GUIDES
DOWNLOAD A GUIDE
FAQ